Board Component
A board component on your machine communicates with the other components of the machine.
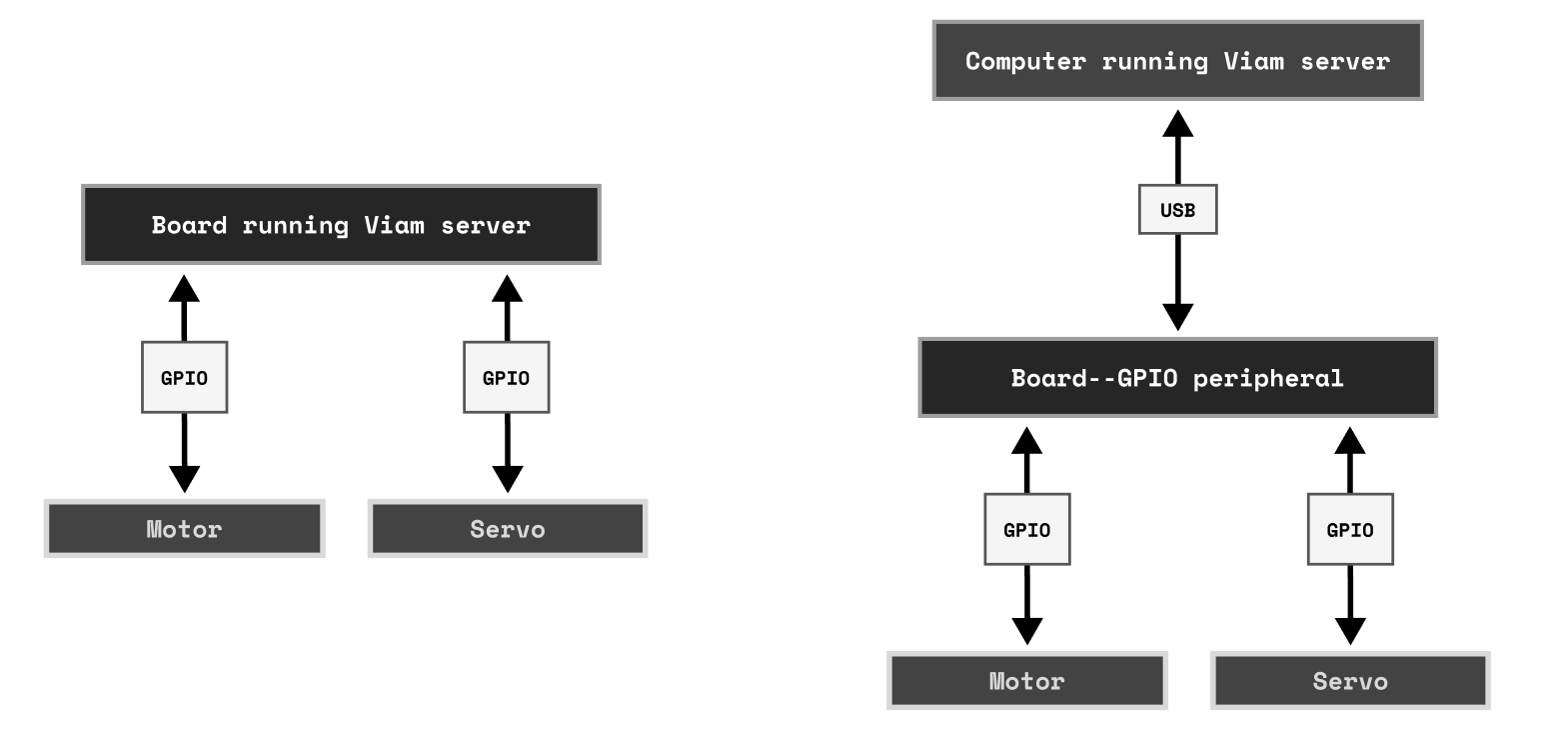
A board can be:
- A single-board computer (SBC) with GPIO pins and a CPU capable of running
viam-server. - A GPIO peripheral device that must connect to an external computer.
- A PWM peripheral device that must connect to an SBC that has a CPU and GPIO pins.
The board of a machine is also its signal wire hub that provides access to general purpose input/output (GPIO) pins: a collection of pins on the motherboard of a computer that can receive electrical signals.
Signaling is overseen by a computer running viam-server which allows you to control the flow of electricity to these pins to change their state between “high” (active) and “low” (inactive), and wire them to send digital signals to and from other hardware.
Available models
Running viam-server
The board component allows you to use the pins on your board. If there is no board model for your board:
- you can still run
viam-serverif your board supports it - you can still access USB ports
For some SBCs, for example the RockPi S, you can use the pins on your board with an experimental periph.io based modular component.
To use your board component, check whether one of the following models supports it.
For configuration information, click on the model name:
Add support for other models
If none of the existing models fit your use case, you can create a modular resource to add support for it.
| Model | Description |
|---|---|
esp32 | An ESP32 microcontroller |
Add support for other models
If none of the existing models fit your use case, you can create a modular resource to add support for it.
viam-micro-server works differently from the RDK, so creating modular resources for it is different.
Refer to the Micro-RDK Module Template on GitHub for information on how to create custom resources for your viam-micro-server machine.
You will need to recompile and flash your ESP32 yourself instead of using Viam’s prebuilt binary and installer.
Control your board with Viam’s client SDK libraries
To get started using Viam’s SDKs to connect to and control your machine, go to your machine’s page on the Viam app, navigate to the CONNECT tab’s Code sample page, select your preferred programming language, and copy the sample code.
API key and API key ID
By default, the sample code does not include your machine API key and API key ID. We strongly recommend that you add your API key and API key ID as an environment variable and import this variable into your development environment as needed.
To show your machine’s API key and API key ID in the sample code, toggle Include API key on the CONNECT tab’s Code sample page.
Caution
Do not share your API key or machine address publicly. Sharing this information could compromise your system security by allowing unauthorized access to your machine, or to the computer running your machine.
When executed, this sample code will create a connection to your machine as a client.
Then control your machine programmatically by getting your board component from the machine with FromRobot and adding API method calls, as shown in the following examples.
These examples assume you have a board called “my_board” configured as a component of your machine.
If your board has a different name, change the name in the code.
Be sure to import the board package for the SDK you are using:
from viam.components.board import Board
import (
"go.viam.com/rdk/components/board"
)
API
The board component supports the following methods:
| Method Name | Description | viam-micro-server Support |
|---|---|---|
SetGPIO | Set the digital signal output of this pin to low (0V) or high (active, >0V). | |
GetGPIO | Get if the digital signal output of this pin is high (active, >0V). | |
GetPWM | Get the pin’s pulse-width modulation (PWM) duty cycle: a float [0.0, 1.0] representing the percentage of time the digital signal output by this pin is in the high state (active, >0V) relative to the interval period of the PWM signal (interval period being the mathematical inverse of the PWM frequency). | |
SetPWM | Set the pin’s Pulse-width modulation (PWM) duty cycle: a float [0.0, 1.0] indicating the percentage of time the digital signal output of this pin is in the high state (active, >0V) relative to the interval period of the PWM signal (interval period being the mathematical inverse of the PWM frequency). | |
PWMFrequency | Get the PWM frequency of the GPIO pin. | |
SetPWMFrequency | Set the pin to the given PWM frequency (in Hz). When frequency is 0, it will use the board’s default PWM frequency. | |
AnalogNames | Get the name of every configured Analog on the board. | |
AnalogByName | Get a configured Analog by name. | |
Write | Write an analog value to a pin on the board. | |
GetDigitalInterruptValue | Get a configured DigitalInterrupt by name. | |
StreamTicks | Start a stream of DigitalInterrupt ticks. | |
SetPowerMode | Set the board to the indicated PowerMode. | |
GetGeometries | Get all the geometries associated with the board in its current configuration, in the frame of the board. | |
Read | Read the current integer value of the digital signal output by the ADC. | |
Value | Get the current value of this interrupt. | |
DigitalInterruptNames | Get the name of every configured DigitalInterrupt on the board. | |
GPIOPinByName | Get a GPIOPin by pin number. | |
Reconfigure | Reconfigure this resource. | |
DoCommand | Execute model-specific commands that are not otherwise defined by the component API. | |
FromRobot | Get the resource from the provided robot with the given name. | |
Name | Get the name of the digital interrupt. | |
GetResourceName | Get the ResourceName for this board with the given name. | |
Close | Safely shut down the resource and prevent further use. |
SetGPIO
Set the digital signal output of this pin to low (0V) or high (active, >0V).
Supported by viam-micro-server.
Parameters:
high(bool) (required): When true, sets the pin to high. When false, sets the pin to low.extra(Mapping[str, Any]) (optional): Extra options to pass to the underlying RPC call.timeout(float) (optional): An option to set how long to wait (in seconds) before calling a time-out and closing the underlying RPC call.
Returns:
- None.
Example:
my_board = Board.from_robot(robot=robot, name="my_board")
# Get the GPIOPin with pin number 15.
pin = await my_board.gpio_pin_by_name(name="15")
# Set the pin to high.
await pin.set(high="true")
For more information, see the Python SDK Docs.
Parameters:
ctx(Context): A Context carries a deadline, a cancellation signal, and other values across API boundaries.high(bool): Iftrue, set the state of the pin to high. Iffalse, set the state of the pin to low.extra(map[string]interface{}): Extra options to pass to the underlying RPC call.
Returns:
- (error): An error, if one occurred.
Example:
myBoard, err := board.FromRobot(robot, "my_board")
// Get the GPIOPin with pin number 15.
pin, err := myBoard.GPIOPinByName("15")
// Set the pin to high.
err := pin.Set(context.Background(), "true", nil)
For more information, see the Go SDK Docs.
GetGPIO
Get if the digital signal output of this pin is high (active, >0V).
Supported by viam-micro-server.
Parameters:
extra(Mapping[str, Any]) (optional): Extra options to pass to the underlying RPC call.timeout(float) (optional): An option to set how long to wait (in seconds) before calling a time-out and closing the underlying RPC call.
Returns:
- (bool): Indicates if the state of the pin is high.
Example:
my_board = Board.from_robot(robot=robot, name="my_board")
# Get the GPIOPin with pin number 15.
pin = await my_board.gpio_pin_by_name(name="15")
# Get if it is true or false that the state of the pin is high.
high = await pin.get()
For more information, see the Python SDK Docs.
Parameters:
ctx(Context): A Context carries a deadline, a cancellation signal, and other values across API boundaries.extra(map[string]interface{}): Extra options to pass to the underlying RPC call.
Returns:
- (bool): If
true, the state of the pin is high. Iffalse, the state of the pin is low. - (error): An error, if one occurred.
Example:
myBoard, err := board.FromRobot(robot, "my_board")
// Get the GPIOPin with pin number 15.
pin, err := myBoard.GPIOPinByName("15")
// Get if it is true or false that the state of the pin is high.
high := pin.Get(context.Background(), nil)
For more information, see the Go SDK Docs.
GetPWM
Info
Pulse-width modulation (PWM) is a method where of transmitting a digital signal in the form of pulses to control analog circuits. With PWM on a board, the continuous digital signal output by a GPIO pin is sampled at regular intervals and transmitted to any hardware components wired to the pin that read analog signals. This enables the board to communicate with these components.
Get the pin’s pulse-width modulation (PWM) duty cycle: a float [0.0, 1.0] representing the percentage of time the digital signal output by this pin is in the high state (active, >0V) relative to the interval period of the PWM signal (interval period being the mathematical inverse of the PWM frequency).
Supported by viam-micro-server.
Parameters:
extra(Mapping[str, Any]) (optional): Extra options to pass to the underlying RPC call.timeout(float) (optional): An option to set how long to wait (in seconds) before calling a time-out and closing the underlying RPC call.
Returns:
- (float): The duty cycle.
Example:
my_board = Board.from_robot(robot=robot, name="my_board")
# Get the GPIOPin with pin number 15.
pin = await my_board.gpio_pin_by_name(name="15")
# Get if it is true or false that the state of the pin is high.
duty_cycle = await pin.get_pwm()
For more information, see the Python SDK Docs.
Parameters:
ctx(Context): A Context carries a deadline, a cancellation signal, and other values across API boundaries.extra(map[string]interface{}): Extra options to pass to the underlying RPC call.
Returns:
- (float64): A float [
0.0,1.0] representing the percentage of time the digital signal output by this pin is in the high state relative to the interval period of the PWM signal. - (error): An error, if one occurred.
Example:
myBoard, err := board.FromRobot(robot, "my_board")
// Get the GPIOPin with pin number 15.
pin, err := myBoard.GPIOPinByName("15")
// Returns the duty cycle.
duty_cycle := pin.PWM(context.Background(), nil)
For more information, see the Go SDK Docs.
SetPWM
Set the pin’s Pulse-width modulation (PWM) duty cycle: a float [0.0, 1.0] indicating the percentage of time the digital signal output of this pin is in the high state (active, >0V) relative to the interval period of the PWM signal (interval period being the mathematical inverse of the PWM frequency).
Supported by viam-micro-server.
Parameters:
duty_cycle(float) (required): The duty cycle.extra(Mapping[str, Any]) (optional): Extra options to pass to the underlying RPC call.timeout(float) (optional): An option to set how long to wait (in seconds) before calling a time-out and closing the underlying RPC call.
Returns:
- None.
Example:
my_board = Board.from_robot(robot=robot, name="my_board")
# Get the GPIOPin with pin number 15.
pin = await my_board.gpio_pin_by_name(name="15")
# Set the duty cycle to .6, meaning that this pin will be in the high state for
# 60% of the duration of the PWM interval period.
await pin.set_pwm(cycle=.6)
For more information, see the Python SDK Docs.
Parameters:
ctx(Context): A Context carries a deadline, a cancellation signal, and other values across API boundaries.dutyCyclePct(float64): A float [0.0,1.0] representing the percentage of time the digital signal output by this pin is in the high state relative to the interval period of the PWM signal.extra(map[string]interface{}): Extra options to pass to the underlying RPC call.
Returns:
- (error): An error, if one occurred.
Example:
myBoard, err := board.FromRobot(robot, "my_board")
// Get the GPIOPin with pin number 15.
pin, err := myBoard.GPIOPinByName("15")
// Set the duty cycle to .6, meaning that this pin will be in the high state for 60% of the duration of the PWM interval period.
err := pin.SetPWM(context.Background(), .6, nil)
For more information, see the Go SDK Docs.
PWMFrequency
Get the PWM frequency of the GPIO pin.
Supported by viam-micro-server.
Parameters:
extra(Mapping[str, Any]) (optional): Extra options to pass to the underlying RPC call.timeout(float) (optional): An option to set how long to wait (in seconds) before calling a time-out and closing the underlying RPC call.
Returns:
- (int): The PWM frequency.
Example:
my_board = Board.from_robot(robot=robot, name="my_board")
# Get the GPIOPin with pin number 15.
pin = await my_board.gpio_pin_by_name(name="15")
# Get the PWM frequency of this pin.
freq = await pin.get_pwm_frequency()
For more information, see the Python SDK Docs.
Parameters:
ctx(Context): A Context carries a deadline, a cancellation signal, and other values across API boundaries.extra(map[string]interface{}): Extra options to pass to the underlying RPC call.
Returns:
- (uint): The PWM Frequency in Hertz (Hz) (the count of PWM interval periods per second) the digital signal output by this pin is set to.
- (error): An error, if one occurred.
Example:
myBoard, err := board.FromRobot(robot, "my_board")
// Get the GPIOPin with pin number 15.
pin, err := myBoard.GPIOPinByName("15")
// Get the PWM frequency of this pin.
freqHz, err := pin.PWMFreq(context.Background(), nil)
For more information, see the Go SDK Docs.
SetPWMFrequency
Set the pin to the given PWM frequency (in Hz). When frequency is 0, it will use the board’s default PWM frequency.
Note
If you attempt to set an unsupported PWM frequency on an esp32, the frequency will revert to the last valid frequency.
This may restart the PWM signal.
viam-micro-server.Parameters:
frequency(int) (required): The frequency, in Hz.extra(Mapping[str, Any]) (optional): Extra options to pass to the underlying RPC call.timeout(float) (optional): An option to set how long to wait (in seconds) before calling a time-out and closing the underlying RPC call.
Returns:
- None.
Example:
my_board = Board.from_robot(robot=robot, name="my_board")
# Get the GPIOPin with pin number 15.
pin = await my_board.gpio_pin_by_name(name="15")
# Set the PWM frequency of this pin to 1600 Hz.
high = await pin.set_pwm_frequency(frequency=1600)
For more information, see the Python SDK Docs.
Parameters:
ctx(Context): A Context carries a deadline, a cancellation signal, and other values across API boundaries.freqHz(uint): The PWM Frequency in Hertz (Hz), the count of PWM interval periods per second, to set the digital signal output by this pin to.extra(map[string]interface{}): Extra options to pass to the underlying RPC call.
Returns:
- (error): An error, if one occurred.
Example:
myBoard, err := board.FromRobot(robot, "my_board")
// Get the GPIOPin with pin number 15.
pin, err := myBoard.GPIOPinByName("15")
// Set the PWM frequency of this pin to 1600 Hz.
high := pin.SetPWMFreq(context.Background(), 1600, nil)
For more information, see the Go SDK Docs.
AnalogNames
Get the name of every configured Analog on the board.
Parameters:
- None.
Returns:
- (List[str]): The list of names of all known analog readers/writers.
Example:
my_board = Board.from_robot(robot=robot, name="my_board")
# Get the name of every Analog configured on the board.
names = await my_board.analog_names()
For more information, see the Python SDK Docs.
Parameters:
- None.
Returns:
- ([]string): A slice containing the
"name"of every analog pin configured on the board.
For more information, see the Go SDK Docs.
AnalogByName
Get a configured Analog by name.
Parameters:
name(str) (required): Name of the analog reader to be retrieved.
Returns:
- (viam.components.board.board.Board.Analog): The analog reader or writer.
Example:
my_board = Board.from_robot(robot=robot, name="my_board")
# Get the Analog "my_example_analog_reader".
reader = await my_board.analog_by_name(name="my_example_analog_reader")
For more information, see the Python SDK Docs.
Parameters:
name(string): Name of the analog pin you want to retrieve. Set as the"name"property in board configuration.
Returns:
- (Analog): An interface representing an analog pin configured and residing on the board.
- (error): An error, if one occurred.
Example:
myBoard, err := board.FromRobot(robot, "my_board")
// Get the Analog pin "my_example_analog".
analog, err := myBoard.AnalogByName("my_example_analog")
For more information, see the Go SDK Docs.
Parameters:
Returns:
Example:
// Get the current value of an analog reader named "my_example_analog"
var analogVal = await myBoard.analogReaderValue('my_example_analog');
For more information, see the Flutter SDK Docs.
Write
Write an analog value to a pin on the board.
Supported by viam-micro-server.
Parameters:
ctx(Context): A Context carries a deadline, a cancellation signal, and other values across API boundaries.value(int): Value to write to the pin.extra(map[string]interface{}): Extra options to pass to the underlying RPC call.
Returns:
- (error): An error, if one occurred.
Example:
myBoard, err := board.FromRobot(robot, "my_board")
// Get the Analog pin "my_example_analog".
analog, err := myBoard.AnalogByName("my_example_analog")
// Set the pin to value 48.
err := analog.Write(context.Background(), 48, nil)
For more information, see the Go SDK Docs.
GetDigitalInterruptValue
Get a configured DigitalInterrupt by name.
Parameters:
name(str) (required): Name of the digital interrupt.
Returns:
- (viam.components.board.board.Board.DigitalInterrupt): The digital interrupt.
Example:
my_board = Board.from_robot(robot=robot, name="my_board")
# Get the DigitalInterrupt "my_example_digital_interrupt".
interrupt = await my_board.digital_interrupt_by_name(
name="my_example_digital_interrupt")
For more information, see the Python SDK Docs.
Parameters:
name(string): Name of the digital interrupt you want to retrieve. Set as the"name"property in board configuration.
Returns:
- (DigitalInterrupt): An interface representing a configured interrupt on the board.
- (error): An error, if one occurred.
Example:
myBoard, err := board.FromRobot(robot, "my_board")
// Get the DigitalInterrupt "my_example_digital_interrupt".
interrupt, err := myBoard.DigitalInterruptByName("my_example_digital_interrupt")
For more information, see the Go SDK Docs.
StreamTicks
Start a stream of DigitalInterrupt ticks.
Parameters:
interrupts(List[viam.components.board.board.Board.DigitalInterrupt]) (required): list of digital interrupts to receive ticks from.extra(Mapping[str, Any]) (optional): Extra options to pass to the underlying RPC call.
Returns:
- (viam.components.board.board.TickStream): stream of ticks.
Example:
my_board = Board.from_robot(robot=robot, name="my_board")
di8 = await my_board.digital_interrupt_by_name(name="8"))
di11 = await my_board.digital_interrupt_by_name(name="11"))
# Iterate over stream of ticks from pins 8 and 11.
async for tick in await my_board.stream_ticks([di8, di11]):
print(f"Pin {tick.pin_name} changed to {'high' if tick.high else 'low'} at {tick.time}")
For more information, see the Python SDK Docs.
Parameters:
ctx(Context): A Context carries a deadline, a cancellation signal, and other values across API boundaries.interrupts([]DigitalInterrupt): Slice of digital interrupts to receive ticks from.ch chan(Tick): The channel to stream Ticks, structs containingName,High, andTimestampNanosecfields.extra(map[string]interface{}): Extra options to pass to the underlying RPC call.
Returns:
- (error): An error, if one occurred.
Example:
myBoard, err := board.FromRobot(robot, "my_board")
// Make a channel to stream ticks
ticksChan := make(chan board.Tick)
interrupts := []*DigitalInterrupt{}
if di8, err := myBoard.DigitalInterruptByName("8"); err == nil {
interrupts = append(interrupts, di8)
}
if di11, err := myBoard.DigitalInterruptByName("11"); err == nil {
interrupts = append(interrupts, di11)
}
err = myBoard.StreamTicks(context.Background(), interrupts, ticksChan, nil)
For more information, see the Go SDK Docs.
Parameters:
Returns:
Example:
// Stream ticks from digital interrupts on pins 8 and 11
var interrupts = ['8', '11'];
Stream<Tick> tickStream = await myBoard.streamTicks(interrupts);
For more information, see the Flutter SDK Docs.
SetPowerMode
Set the board to the indicated PowerMode.
Info
This method may not receive a successful response from gRPC when you set the board to the offline power mode PowerMode.POWER_MODE_OFFLINE_DEEP.
When this is the case for your board model, the call is returned with an error specifying that the remote procedure call timed out or that the endpoint is no longer available. This is expected: the board has been successfully powered down and can no longer respond to messages.
Parameters:
mode(viam.proto.component.board.PowerMode.ValueType) (required): The desired power mode.duration(datetime.timedelta) (optional): Requested duration to stay in power mode.timeout(float) (optional): An option to set how long to wait (in seconds) before calling a time-out and closing the underlying RPC call.
Returns:
- None.
Example:
my_board = Board.from_robot(robot=robot, name="my_board")
# Set the power mode of the board to OFFLINE_DEEP.
status = await my_board.set_power_mode(mode=PowerMode.POWER_MODE_OFFLINE_DEEP)
For more information, see the Python SDK Docs.
Parameters:
ctx(Context): A Context carries a deadline, a cancellation signal, and other values across API boundaries.mode(pb.PowerMode): Options to specify power usage of the board:boardpb.PowerMode_POWER_MODE_UNSPECIFIED,boardpb.PowerMode_POWER_MODE_NORMAL, andboardpb.PowerMode_POWER_MODE_OFFLINE_DEEP.duration(*time.Duration): If provided, the board will exit the given power mode after the specified duration.
Returns:
- (error): An error, if one occurred.
Example:
myBoard, err := board.FromRobot(robot, "my_board")
Set the power mode of the board to OFFLINE_DEEP.
myBoard.SetPowerMode(context.Background(), boardpb.PowerMode_POWER_MODE_OFFLINE_DEEP, nil)
For more information, see the Go SDK Docs.
Parameters:
powerModePowerMode (required)secondsint (required)nanosint (required)extraMap<String, dynamic>? (optional)
Returns:
- Future<void>
Example:
// Set the power mode of the board to offline deep for 60 seconds
// Requires importing 'package:viam_sdk/protos/component/board.dart'
const powerMode = PowerMode.POWER_MODE_OFFLINE_DEEP;
await myBoard.setPowerMode(powerMode, 60, 0);
For more information, see the Flutter SDK Docs.
GetGeometries
Get all the geometries associated with the board in its current configuration, in the frame of the board. The motion and navigation services use the relative position of inherent geometries to configured geometries representing obstacles for collision detection and obstacle avoidance while motion planning.
Parameters:
extra(Mapping[str, Any]) (optional): Extra options to pass to the underlying RPC call.timeout(float) (optional): An option to set how long to wait (in seconds) before calling a time-out and closing the underlying RPC call.
Returns:
- (List[viam.proto.common.Geometry]): The geometries associated with the Component.
Example:
geometries = await component.get_geometries()
if geometries:
# Get the center of the first geometry
print(f"Pose of the first geometry's centerpoint: {geometries[0].center}")
For more information, see the Python SDK Docs.
Read
Read the current integer value of the digital signal output by the ADC.
Supported by viam-micro-server.
Parameters:
extra(Mapping[str, Any]) (optional): Extra options to pass to the underlying RPC call.timeout(float) (optional): An option to set how long to wait (in seconds) before calling a time-out and closing the underlying RPC call.
Returns:
- (viam.components.board.board.Board.Analog.Value): The current value, including the min, max, and step_size of the reader.
Example:
my_board = Board.from_robot(robot=robot, name="my_board")
# Get the Analog "my_example_analog_reader".
reader = await my_board.analog_reader_by_name(
name="my_example_analog_reader")
# Get the value of the digital signal "my_example_analog_reader" has most
# recently measured.
reading = await reader.read()
For more information, see the Python SDK Docs.
Parameters:
ctx(Context): A Context carries a deadline, a cancellation signal, and other values across API boundaries.extra(map[string]interface{}): Extra options to pass to the underlying RPC call.
Returns:
- (AnalogValue): The current value, including the integer
Valueof the digital signal output by the analog pin and theMin,Max, andStepSizeof the reader. - (error): An error, if one occurred.
Example:
myBoard, err := board.FromRobot(robot, "my_board")
// Get the analog pin "my_example_analog".
analog, err := myBoard.AnalogByName("my_example_analog")
// Get the value of the analog signal "my_example_analog" has most recently measured.
reading, err := analog.Read(context.Background(), nil)
readingValue := reading.Value
stepSize := reading.StepSize
For more information, see the Go SDK Docs.
Value
Get the current value of this interrupt.
Parameters:
extra(Mapping[str, Any]) (optional): Extra options to pass to the underlying RPC call.timeout(float) (optional): An option to set how long to wait (in seconds) before calling a time-out and closing the underlying RPC call.
Returns:
- (int): The current value.
Example:
my_board = Board.from_robot(robot=robot, name="my_board")
# Get the DigitalInterrupt "my_example_digital_interrupt".
interrupt = await my_board.digital_interrupt_by_name(
name="my_example_digital_interrupt")
# Get the amount of times this DigitalInterrupt has been interrupted with a
# tick.
count = await interrupt.value()
For more information, see the Python SDK Docs.
Parameters:
ctx(Context): A Context carries a deadline, a cancellation signal, and other values across API boundaries.extra(map[string]interface{}): Extra options to pass to the underlying RPC call.
Returns:
Example:
myBoard, err := board.FromRobot(robot, "my_board")
// Get the DigitalInterrupt "my_example_digital_interrupt".
interrupt, err := myBoard.DigitalInterruptByName("my_example_digital_interrupt")
// Get the amount of times this DigitalInterrupt has ticked.
count, err := interrupt.Value(context.Background(), nil)
For more information, see the Go SDK Docs.
Parameters:
Returns:
Example:
// Get the current value of a digital interrupt named "my_example_digital_interrupt"
var interruptVal = await myBoard.digitalInterruptValue('my_example_digital_interrupt');
For more information, see the Flutter SDK Docs.
DigitalInterruptNames
Get the name of every configured DigitalInterrupt on the board.
Parameters:
- None.
Returns:
- (List[str]): The names of the digital interrupts.
Example:
my_board = Board.from_robot(robot=robot, name="my_board")
# Get the name of every DigitalInterrupt configured on the board.
names = await my_board.digital_interrupt_names()
For more information, see the Python SDK Docs.
Parameters:
- None.
Returns:
- ([]string): A slice containing the
"name"of every interrupt configured on the board.
For more information, see the Go SDK Docs.
GPIOPinByName
Get a GPIOPin by pin number.
Parameters:
name(str) (required): Name of the GPIO pin.
Returns:
- (viam.components.board.board.Board.GPIOPin): The pin.
Example:
my_board = Board.from_robot(robot=robot, name="my_board")
# Get the GPIOPin with pin number 15.
pin = await my_board.gpio_pin_by_name(name="15")
For more information, see the Python SDK Docs.
Parameters:
name(string): Pin number of the GPIO pin you want to retrieve as aGPIOPininterface. Refer to the pinout diagram and data sheet of your board model for pin numbers.
Returns:
- (GPIOPin): An interface representing an individual GPIO pin on the board.
- (error): An error, if one occurred.
Example:
myBoard, err := board.FromRobot(robot, "my_board")
// Get the GPIOPin with pin number 15.
pin, err := myBoard.GPIOPinByName("15")
For more information, see the Go SDK Docs.
Reconfigure
Reconfigure this resource. Reconfigure must reconfigure the resource atomically and in place.
Parameters:
ctx(Context): A Context carries a deadline, a cancellation signal, and other values across API boundaries.deps(Dependencies): The resource dependencies.conf(Config): The resource configuration.
Returns:
- (error): An error, if one occurred.
For more information, see the Go SDK Docs.
DoCommand
Execute model-specific commands that are not otherwise defined by the component API.
For built-in models, model-specific commands are covered with each model’s documentation.
If you are implementing your own board and add features that have no built-in API method, you can access them with DoCommand.
Supported by viam-micro-server.
Parameters:
command(Mapping[str, ValueTypes]) (required): The command to execute.timeout(float) (optional): An option to set how long to wait (in seconds) before calling a time-out and closing the underlying RPC call.
Returns:
- (Mapping[str, viam.utils.ValueTypes]): Result of the executed command.
Raises:
- (NotImplementedError): Raised if the Resource does not support arbitrary commands.
Example:
command = {"cmd": "test", "data1": 500}
result = component.do(command)
For more information, see the Python SDK Docs.
Parameters:
ctx(Context): A Context carries a deadline, a cancellation signal, and other values across API boundaries.cmd(map[string]interface{}): The command to execute.
Returns:
- (map[string]interface{}): The command response.
- (error): An error, if one occurred.
Example:
// This example shows using DoCommand with an arm component.
myArm, err := arm.FromRobot(machine, "my_arm")
command := map[string]interface{}{"cmd": "test", "data1": 500}
result, err := myArm.DoCommand(context.Background(), command)
For more information, see the Go SDK Docs.
FromRobot
Get the resource from the provided robot with the given name.
Parameters:
robotRobotClient (required)nameString (required)
Returns:
For more information, see the Flutter SDK Docs.
Name
Get the name of the digital interrupt.
Parameters:
- None.
Returns:
- (string): The name of the digital interrupt.
For more information, see the Go SDK Docs.
GetResourceName
Get the ResourceName for this board with the given name.
Parameters:
name(str) (required): The name of the Resource.
Returns:
- (viam.proto.common.ResourceName): The ResourceName of this Resource.
Example:
# Can be used with any resource, using an arm as an example
my_arm_name = my_arm.get_resource_name("my_arm")
For more information, see the Python SDK Docs.
Close
Safely shut down the resource and prevent further use.
Parameters:
- None.
Returns:
- None.
Example:
await component.close()
For more information, see the Python SDK Docs.
Parameters:
ctx(Context): A Context carries a deadline, a cancellation signal, and other values across API boundaries.
Returns:
- (error): An error, if one occurred.
Example:
// This example shows using Close with an arm component.
myArm, err := arm.FromRobot(machine, "my_arm")
err = myArm.Close(ctx)
For more information, see the Go SDK Docs.
Troubleshooting
You can find additional assistance in the Troubleshooting section.
You can also ask questions in the Community Discord and we will be happy to help.
Next steps
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! If you have any other feedback please let us know:
We're sorry about that. To help us improve, please tell us what we can do better:
Thank you!