SLAM Service
Stability Notice
The SLAM service is an experimental feature. Stability is not guaranteed. Breaking changes are likely to occur, and occur often.
Simultaneous Localization And Mapping (SLAM) allows your machine to create a map of its surroundings and find its location within that map. SLAM is an important area of ongoing research in robotics, particularly for mobile applications such as drones, boats, and rovers.
The Viam SLAM service supports the integration of SLAM as a service on your machine. You can conduct SLAM with data collected live by a RPlidar or with LIDAR data you provide in configuration, and easily view the map you build by clicking on View SLAM library on your location’s page in the Viam app:
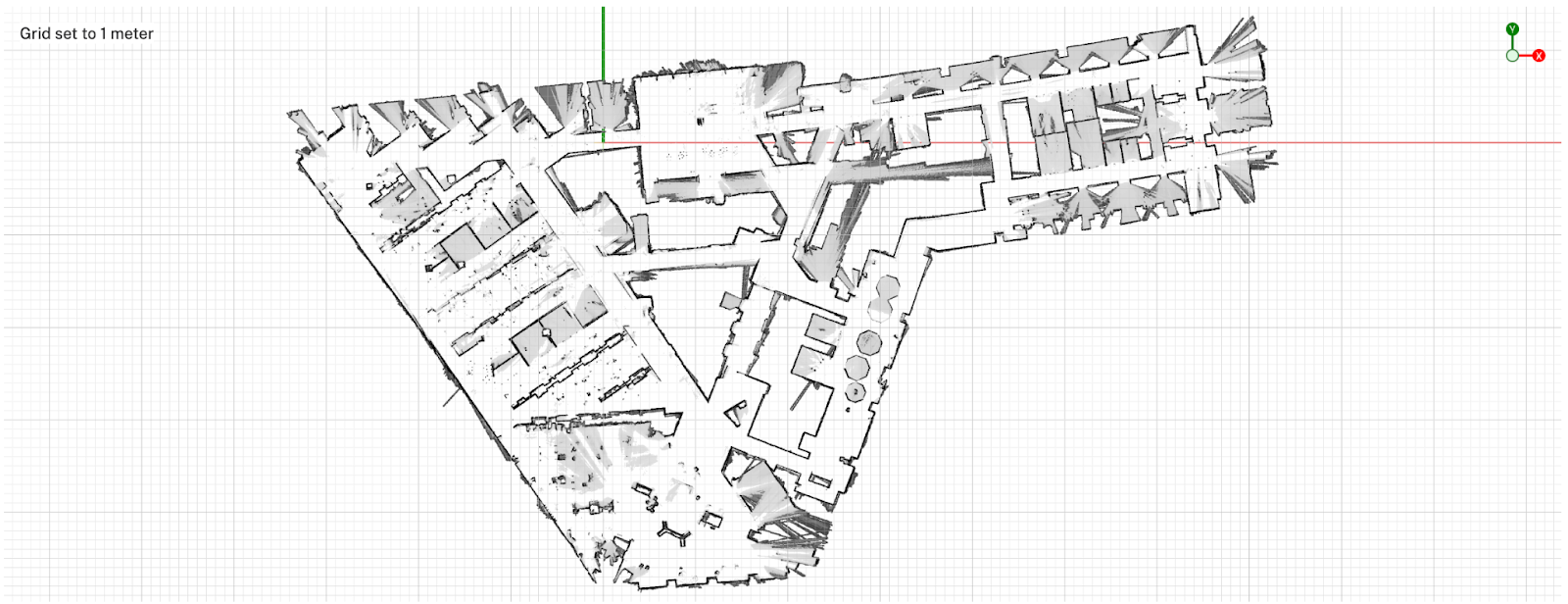
Used with
* Required for use
Configuration
Integrated SLAM libraries include the following. Click the model name for configuration instructions.
| Model | Description |
|---|---|
viam:slam:cartographer | The Cartographer Project performs dense SLAM using LIDAR data. |
viam:cloudslam-wrapper:cloudslam | cloudslam-wrapper Allows you to run supported SLAM algorithms in the cloud. |
API
The SLAM service supports the following methods:
| Method Name | Description |
|---|---|
GetPosition | Get the current position of the component the SLAM service is configured to source point cloud data from in the SLAM map as a Pose. |
GetPointCloudMap | Get the point cloud map. |
GetInternalState | Get the internal state of the SLAM algorithm required to continue mapping/localization. |
GetProperties | Get information about the current SLAM session. |
InternalStateFull | InternalStateFull concatenates the streaming responses from InternalState into the internal serialized state of the SLAM algorithm. |
PointCloudMapFull | PointCloudMapFull concatenates the streaming responses from PointCloudMap into a full point cloud. |
Reconfigure | Reconfigure this resource. |
DoCommand | Execute model-specific commands that are not otherwise defined by the service API. |
GetResourceName | Get the ResourceName for this instance of the SLAM service with the given name. |
Close | Safely shut down the resource and prevent further use. |
Tip
The following code examples assume that you have a machine configured with a SLAM service called "my_slam_service", and that you add the required code to connect to your machine and import any required packages at the top of your code file.
Go to your machine’s CONNECT tab on the Viam app and select the Code sample page for sample code to connect to your machine.
GetPosition
Get the current position of the component the SLAM service is configured to source point cloud data from in the SLAM map as a Pose.
Parameters:
timeout(float) (optional): An option to set how long to wait (in seconds) before calling a time-out and closing the underlying RPC call.
Returns:
- (viam.services.slam.Pose): The current position of the specified component.
Example:
slam_svc = SLAMClient.from_robot(robot=robot, name="my_slam_service")
# Get the current position of the specified source component in the SLAM map as a Pose.
pose = await slam.get_position()
For more information, see the Python SDK Docs.
Parameters:
ctx(Context): A Context carries a deadline, a cancellation signal, and other values across API boundaries.
Returns:
- (spatialmath.Pose): A
Poserepresenting the current position of the specified component. - (error): An error, if one occurred.
Example:
// Get the current position of the specified source component
// in the SLAM map as a Pose.
pos, name, err := mySLAMService.Position(context.Background())
For more information, see the Go SDK Docs.
GetPointCloudMap
Get the point cloud map.
Parameters:
return_edited_map(bool) (required): signal to the SLAM service to return an edited map, if the map package contains one and if the SLAM service supports the feature.timeout(float) (optional): An option to set how long to wait (in seconds) before calling a time-out and closing the underlying RPC call.
Returns:
- (List[bytes]): Complete pointcloud in standard PCD format. Chunks of the PointCloud, concatenating all GetPointCloudMapResponse.point_cloud_pcd_chunk values.
Example:
slam_svc = SLAMClient.from_robot(robot=robot, name="my_slam_service")
# Get the point cloud map in standard PCD format.
pcd_map = await slam_svc.get_point_cloud_map()
For more information, see the Python SDK Docs.
GetInternalState
Get the internal state of the SLAM algorithm required to continue mapping/localization.
Parameters:
timeout(float) (optional): An option to set how long to wait (in seconds) before calling a time-out and closing the underlying RPC call.
Returns:
- (List[bytes]): Chunks of the internal state of the SLAM algorithm.
Example:
slam = SLAMClient.from_robot(robot=robot, name="my_slam_service")
# Get the internal state of the SLAM algorithm required to continue mapping/localization.
internal_state = await slam.get_internal_state()
For more information, see the Python SDK Docs.
GetProperties
Get information about the current SLAM session.
Parameters:
timeout(float) (optional): An option to set how long to wait (in seconds) before calling a time-out and closing the underlying RPC call.
Returns:
- (viam.services.slam.slam.SLAM.Properties): The properties of SLAM.
Example:
slam_svc = SLAMClient.from_robot(robot=robot, name="my_slam_service")
# Get the properties of your current SLAM session.
slam_properties = await slam_svc.get_properties()
For more information, see the Python SDK Docs.
Parameters:
ctx(Context): A Context carries a deadline, a cancellation signal, and other values across API boundaries.
Returns:
(Properties): Information about the current SLAM session. An object containing four fields:
SensorInfo(SensorInfo[]): Information about the sensors (camera and movement sensor) configured for your SLAM service, including the name and type of sensor.CloudSlam(bool): A boolean which indicates whether the session is being run in the cloud.MappingMode(MappingMode): Represents the form of mapping and localizing the current session is performing. This includes creating a new map, localizing on an existing map and updating an existing map.InternalStateFileType(string): The file type the service’s internal state algorithm is stored in.
(error): An error, if one occurred.
Example:
// Get the properties of your current SLAM session
properties, err := mySLAMService.Properties(context.Background())
For more information, see the Go SDK Docs.
InternalStateFull
InternalStateFull concatenates the streaming responses from InternalState into the internal serialized state of the SLAM algorithm.
Parameters:
ctx(Context): A Context carries a deadline, a cancellation signal, and other values across API boundaries.slamSvc(Service): The SLAM service name to fetch the internal state for.
Returns:
- ([]byte): A byte value representing the internal serialized state of the SLAM algorithm.
- (error): An error, if one occurred.
For more information, see the Go SDK Docs.
PointCloudMapFull
PointCloudMapFull concatenates the streaming responses from PointCloudMap into a full point cloud.
Parameters:
ctx(Context): A Context carries a deadline, a cancellation signal, and other values across API boundaries.slamSvc(Service): The SLAM service name to fetch the point cloud map for.returnEditedMap(bool): A boolean representing whether to return the edited map (true) or not (false).
Returns:
For more information, see the Go SDK Docs.
Reconfigure
Reconfigure this resource. Reconfigure must reconfigure the resource atomically and in place.
Parameters:
ctx(Context): A Context carries a deadline, a cancellation signal, and other values across API boundaries.deps(Dependencies): The resource dependencies.conf(Config): The resource configuration.
Returns:
- (error): An error, if one occurred.
For more information, see the Go SDK Docs.
DoCommand
Execute model-specific commands that are not otherwise defined by the service API.
For built-in service models, any model-specific commands available are covered with each model’s documentation.
If you are implementing your own SLAM service and add features that have no built-in API method, you can access them with DoCommand.
Parameters:
command(Mapping[str, ValueTypes]) (required): The command to execute.timeout(float) (optional): An option to set how long to wait (in seconds) before calling a time-out and closing the underlying RPC call.
Returns:
- (Mapping[str, viam.utils.ValueTypes]): Result of the executed command.
Example:
service = SERVICE.from_robot(robot, "builtin") # replace SERVICE with the appropriate class
my_command = {
"cmnd": "dosomething",
"someparameter": 52
}
# Can be used with any resource, using the motion service as an example
await service.do_command(command=my_command)
For more information, see the Python SDK Docs.
Parameters:
ctx(Context): A Context carries a deadline, a cancellation signal, and other values across API boundaries.cmd(map[string]interface{}): The command to execute.
Returns:
- (map[string]interface{}): The command response.
- (error): An error, if one occurred.
Example:
// This example shows using DoCommand with an arm component.
myArm, err := arm.FromRobot(machine, "my_arm")
command := map[string]interface{}{"cmd": "test", "data1": 500}
result, err := myArm.DoCommand(context.Background(), command)
For more information, see the Go SDK Docs.
GetResourceName
Get the ResourceName for this instance of the SLAM service with the given name.
Parameters:
name(str) (required): The name of the Resource.
Returns:
- (viam.proto.common.ResourceName): The ResourceName of this Resource.
Example:
# Can be used with any resource, using an arm as an example
my_arm_name = my_arm.get_resource_name("my_arm")
For more information, see the Python SDK Docs.
Close
Safely shut down the resource and prevent further use.
Parameters:
- None.
Returns:
- None.
Example:
await component.close()
For more information, see the Python SDK Docs.
Parameters:
ctx(Context): A Context carries a deadline, a cancellation signal, and other values across API boundaries.
Returns:
- (error): An error, if one occurred.
Example:
// This example shows using Close with an arm component.
myArm, err := arm.FromRobot(machine, "my_arm")
err = myArm.Close(ctx)
For more information, see the Go SDK Docs.
SLAM mapping best practices
The best way to improve map quality is by taking extra care when creating the initial map. While in a slam session, you should:
- turn gently and gradually, completely avoiding sudden quick turns
- make frequent loop closures, arriving back at a previously mapped area so the machine can correct for errors in the map layout
- stay relatively (but not extremely) close to walls
- use a machine that can go smoothly over bumps and transitions between flooring areas
- drive at a moderate speed
- when using a wheeled base, try to include an odometry movement sensor. This helps the SLAM algorithm keep track of where the machine is moving.
- it is important to note that the adxl345 accelerometer on the Viam Rover 1 will not satisfy the movement sensor requirement.
You can find additional assistance in the Troubleshooting section.
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! If you have any other feedback please let us know:
We're sorry about that. To help us improve, please tell us what we can do better:
Thank you!