Vision Service
The vision service enables your machine to use its on-board cameras to intelligently see and interpret the world around it. While the camera component lets you access what your machine’s camera sees, the vision service allows you to interpret your image data.
Currently, the vision service supports the following kinds of operations:
To get started with a mini project, see this quickstart guide:
Detections

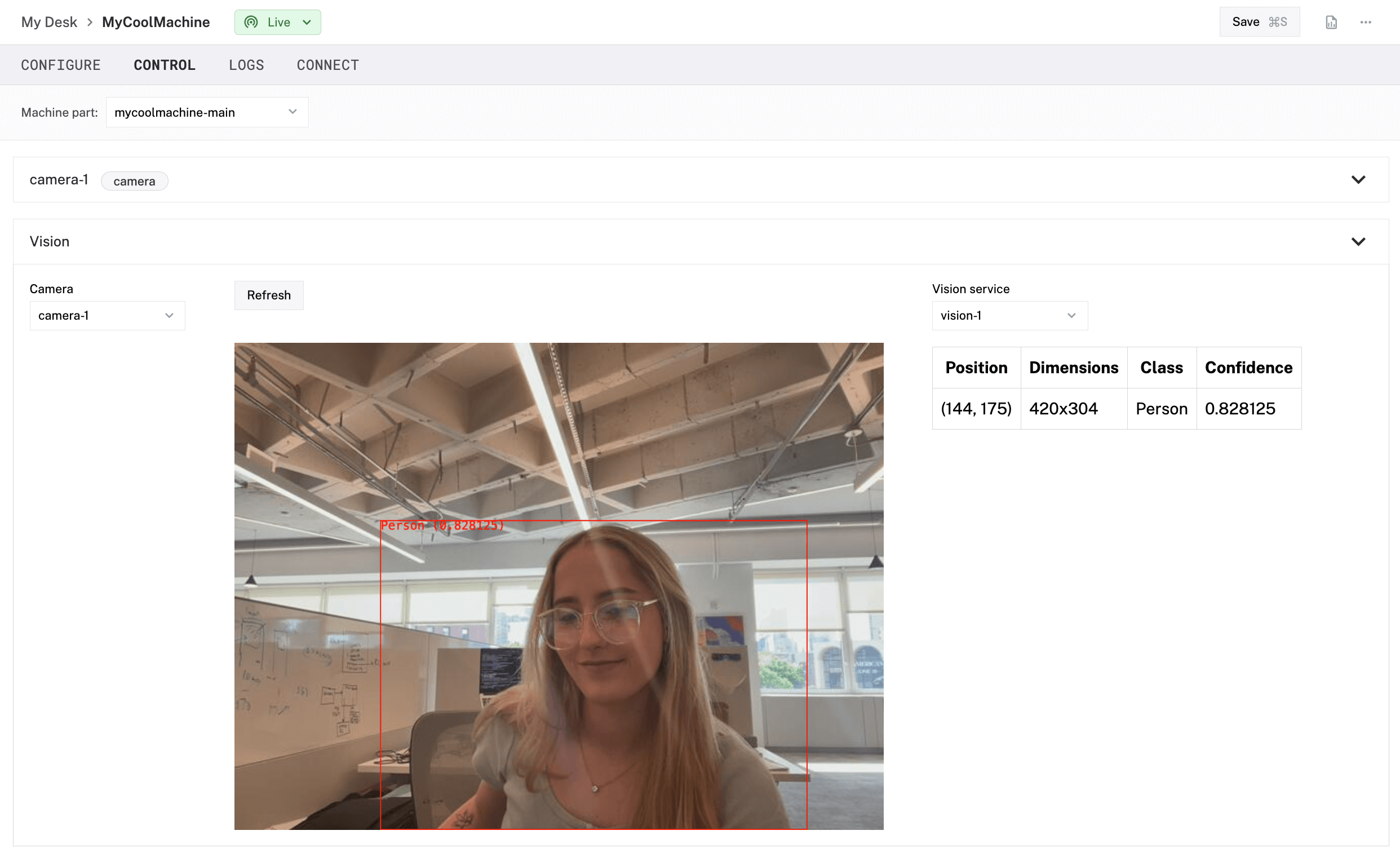
2D Object Detection is the process of taking a 2D image from a camera and identifying and drawing a box around the distinct “objects” of interest in the scene. Any camera that can return 2D images can use 2D object detection.
You can use different types of detectors, both based on heuristics and machine learning, for any object you may need to identify.
The returned detections consist of the bounding box around the identified object, as well as its label and confidence score:
x_min,y_min,x_max,y_max(int): specify the bounding box around the object.class_name(string): specifies the label of the found object.confidence(float): specifies the confidence of the assigned label. Between0.0and1.0, inclusive.
Supported API methods:
Classifications
2D Image Classification is the process of taking a 2D image from a camera and deciding which class label, out of many, best describes the given image. Any camera that can return 2D images can use 2D image classification.
The class labels used for classification vary and depend on the machine learning model and how it was trained.
The returned classifications consist of the image’s class label and confidence score.
class_name(string): specifies the label of the found object.confidence(float): specifies the confidence of the assigned label. Between0.0and1.0, inclusive.
Supported API methods:
Segmentations
3D Object Segmentation is the process of separating and returning a list of the identified “objects” from a 3D scene. The “objects” are usually a list of point clouds with associated metadata, like the label, the 3D bounding box, and center coordinates of the object.
3D object segmentation is useful for obstacle detection. See our guide Navigate with a Rover Base for an example of automating obstacle avoidance with 3D object segmentation for obstacle detection.
Any camera that can return 3D pointclouds can use 3D object segmentation.
Supported API methods:
Available models
For configuration information, click on the model name:
Add support for other models
If none of the existing models fit your use case, you can create a modular resource to add support for it.
Used with
API
Different vision service models support different methods:
| Method Name | Description |
|---|---|
GetDetectionsFromCamera | Get a list of detections from the next image from a specified camera using a configured detector. |
GetDetections | Get a list of detections from a given image using a configured detector. |
GetClassificationsFromCamera | Get a list of classifications from the next image from a specified camera using a configured classifier. |
GetClassifications | Get a list of classifications from a given image using a configured classifier. |
GetObjectPointClouds | Get a list of 3D point cloud objects and associated metadata in the latest picture from a 3D camera (using a specified segmenter). |
CaptureAllFromCamera | Get the next image, detections, classifications, and objects all together, given a camera name. |
Reconfigure | Reconfigure this resource. |
DoCommand | Execute model-specific commands that are not otherwise defined by the service API. |
FromRobot | Get the resource from the provided robot with the given name. |
GetResourceName | Get the ResourceName for this instance of the Vision service with the given name. |
GetProperties | Fetch information about which vision methods a given vision service supports. |
Close | Safely shut down the resource and prevent further use. |
Tip
The following code examples assume that you have a machine configured with a camera and a vision service detector, classifier or segmenter, as applicable, and that you add the required code to connect to your machine and import any required packages at the top of your code file. Go to your machine’s Code sample tab on the Viam app for boilerplate code to connect to your machine.
GetDetectionsFromCamera
Get a list of detections from the next image from a specified camera using a configured detector.
Parameters:
camera_name(str) (required): The name of the camera to use for detection.extra(Mapping[str, Any]) (optional): Extra options to pass to the underlying RPC call.timeout(float) (optional): An option to set how long to wait (in seconds) before calling a time-out and closing the underlying RPC call.
Returns:
- (List[viam.proto.service.vision.Detection]): A list of 2D bounding boxes, their labels, and the confidence score of the labels, around the found objects in the next 2D image from the given camera, with the given detector applied to it.
Raises:
- (ViamError): Raised if given an image without a specified width and height.
Example:
camera_name = "cam1"
# Grab the detector you configured on your machine
my_detector = VisionClient.from_robot(robot, "my_detector")
# Get detections from the next image from the camera
detections = await my_detector.get_detections_from_camera(camera_name)
For more information, see the Python SDK Docs.
Parameters:
ctx(Context): A Context carries a deadline, a cancellation signal, and other values across API boundaries.cameraName(string): The name of the camera from which to get an image to run detections on.extra(map[string]interface{}): Extra options to pass to the underlying RPC call.
Returns:
- ([]objectdetection.Detection): A list of bounding boxes around the detected objects, and confidence scores of those detections.
- (error): An error, if one occurred.
Example:
// Get detections from the camera output
detections, err := visService.DetectionsFromCamera(context.Background(), myCam, nil)
if err != nil {
logger.Fatalf("Could not get detections: %v", err)
}
if len(detections) > 0 {
logger.Info(detections[0])
}
For more information, see the Go SDK Docs.
GetDetections
Get a list of detections from a given image using a configured detector.
Parameters:
image(viam.media.video.ViamImage) (required): The image to get detections from.extra(Mapping[str, Any]) (optional): Extra options to pass to the underlying RPC call.timeout(float) (optional): An option to set how long to wait (in seconds) before calling a time-out and closing the underlying RPC call.
Returns:
- (List[viam.proto.service.vision.Detection]): A list of 2D bounding boxes, their labels, and the confidence score of the labels, around the found objects in the next 2D image from the given camera, with the given detector applied to it.
Raises:
- (ViamError): Raised if given an image without a specified width and height.
Example:
# Grab camera from the machine
cam1 = Camera.from_robot(robot, "cam1")
# Get the detector you configured on your machine
my_detector = VisionClient.from_robot(robot, "my_detector")
# Get an image from the camera
img = await cam1.get_image()
# Get detections from that image
detections = await my_detector.get_detections(img)
For more information, see the Python SDK Docs.
Parameters:
ctx(Context): A Context carries a deadline, a cancellation signal, and other values across API boundaries.img(image.Image): The image in which to look for detections.extra(map[string]interface{}): Extra options to pass to the underlying RPC call.
Returns:
- ([]objectdetection.Detection): A list of 2D bounding boxes around the detected objects, and confidence scores of those detections.
- (error): An error, if one occurred.
Example:
// Get the stream from a camera
camStream, err := myCam.Stream(context.Background())
// Get an image from the camera stream
img, release, err := camStream.Next(context.Background())
defer release()
// Get the detections from the image
detections, err := visService.Detections(context.Background(), img, nil)
if err != nil {
logger.Fatalf("Could not get detections: %v", err)
}
if len(detections) > 0 {
logger.Info(detections[0])
}
For more information, see the Go SDK Docs.
GetClassificationsFromCamera
Get a list of classifications from the next image from a specified camera using a configured classifier.
Parameters:
camera_name(str) (required): The name of the camera to use for detection.count(int) (required): The number of classifications desired.extra(Mapping[str, Any]) (optional): Extra options to pass to the underlying RPC call.timeout(float) (optional): An option to set how long to wait (in seconds) before calling a time-out and closing the underlying RPC call.
Returns:
- (List[viam.proto.service.vision.Classification]): The list of Classifications.
Example:
camera_name = "cam1"
# Grab the classifier you configured on your machine
my_classifier = VisionClient.from_robot(robot, "my_classifier")
# Get the 2 classifications with the highest confidence scores from the next image from the camera
classifications = await my_classifier.get_classifications_from_camera(
camera_name, 2)
For more information, see the Python SDK Docs.
Parameters:
ctx(Context): A Context carries a deadline, a cancellation signal, and other values across API boundaries.cameraName(string): The name of the camera from which to get an image to run the classifier on.n(int): The number of classifications to return. For example, if you specify3you will get the top three classifications with the greatest confidence scores.extra(map[string]interface{}): Extra options to pass to the underlying RPC call.
Returns:
- (classification.Classifications): A list of classification labels, and the confidence scores of those classifications.
- (error): An error, if one occurred.
Example:
// Get the 2 classifications with the highest confidence scores from the camera output
classifications, err := visService.ClassificationsFromCamera(context.Background(), myCam, 2, nil)
if err != nil {
logger.Fatalf("Could not get classifications: %v", err)
}
if len(classifications) > 0 {
logger.Info(classifications[0])
}
For more information, see the Go SDK Docs.
Parameters:
Returns:
Example:
// Example:
var classifications = await myVisionService.classificationsFromCamera('myWebcam', 2);
For more information, see the Flutter SDK Docs.
GetClassifications
Get a list of classifications from a given image using a configured classifier.
Parameters:
image(viam.media.video.ViamImage) (required): The image to get detections from.count(int) (required): The number of classifications desired.extra(Mapping[str, Any]) (optional): Extra options to pass to the underlying RPC call.timeout(float) (optional): An option to set how long to wait (in seconds) before calling a time-out and closing the underlying RPC call.
Returns:
- (List[viam.proto.service.vision.Classification]): The list of Classifications.
Example:
# Grab camera from the machine
cam1 = Camera.from_robot(robot, "cam1")
# Get the classifier you configured on your machine
my_classifier = VisionClient.from_robot(robot, "my_classifier")
# Get an image from the camera
img = await cam1.get_image()
# Get the 2 classifications with the highest confidence scores
classifications = await my_classifier.get_classifications(img, 2)
For more information, see the Python SDK Docs.
Parameters:
ctx(Context): A Context carries a deadline, a cancellation signal, and other values across API boundaries.img(image.Image): The image in which to look for classifications.n(int): The number of classifications to return. For example, if you specify3you will get the top three classifications with the greatest confidence scores.extra(map[string]interface{}): Extra options to pass to the underlying RPC call.
Returns:
- (classification.Classifications): A list of classification labels, and the confidence scores of those classifications.
- (error): An error, if one occurred.
Example:
// Get the stream from a camera
camStream, err := myCam.Stream(context.Background())
if err!=nil {
logger.Error(err)
return
}
// Get an image from the camera stream
img, release, err := camStream.Next(context.Background())
defer release()
// Get the 2 classifications with the highest confidence scores from the image
classifications, err := visService.Classifications(context.Background(), img, 2, nil)
if err != nil {
logger.Fatalf("Could not get classifications: %v", err)
}
if len(classifications) > 0 {
logger.Info(classifications[0])
}
For more information, see the Go SDK Docs.
Parameters:
Returns:
Example:
// Example:
var latestImage = await myWebcam.image();
var classifications = await myVisionService.classifications(latestImage, 2);
For more information, see the Flutter SDK Docs.
GetObjectPointClouds
Get a list of 3D point cloud objects and associated metadata in the latest picture from a 3D camera (using a specified segmenter).
Parameters:
camera_name(str) (required): The name of the camera.extra(Mapping[str, Any]) (optional): Extra options to pass to the underlying RPC call.timeout(float) (optional): An option to set how long to wait (in seconds) before calling a time-out and closing the underlying RPC call.
Returns:
- (List[viam.proto.common.PointCloudObject]): The pointcloud objects with metadata.
Example:
import numpy as np
import open3d as o3d
# Grab the 3D camera from the machine
cam1 = Camera.from_robot(robot, "cam1")
# Grab the object segmenter you configured on your machine
my_segmenter = VisionClient.from_robot(robot, "my_segmenter")
# Get the objects from the camera output
objects = await my_segmenter.get_object_point_clouds(cam1)
# write the first object point cloud into a temporary file
with open("/tmp/pointcloud_data.pcd", "wb") as f:
f.write(objects[0].point_cloud)
pcd = o3d.io.read_point_cloud("/tmp/pointcloud_data.pcd")
points = np.asarray(pcd.points)
For more information, see the Python SDK Docs.
Parameters:
ctx(Context): A Context carries a deadline, a cancellation signal, and other values across API boundaries.cameraName(string): The name of the 3D camera from which to get point cloud data.extra(map[string]interface{}): Extra options to pass to the underlying RPC call.
Returns:
- ([]*viz.Object): A list of point clouds and associated metadata like the center coordinates of each point cloud.
- (error): An error, if one occurred.
Example:
// Get the objects from the camera output
objects, err := visService.GetObjectPointClouds(context.Background(), "cam1", nil)
if err != nil {
logger.Fatalf("Could not get point clouds: %v", err)
}
if len(objects) > 0 {
logger.Info(objects[0])
}
For more information, see the Go SDK Docs.
Parameters:
Returns:
Example:
// Example:
var ptCloud = await myVisionService.objectPointClouds('myCamera');
For more information, see the Flutter SDK Docs.
CaptureAllFromCamera
Get the next image, detections, classifications, and objects all together, given a camera name. Used for visualization.
Parameters:
camera_name(str) (required): The name of the camera to use for detection.return_image(bool) (required): Ask the vision service to return the camera’s latest image.return_classifications(bool) (required): Ask the vision service to return its latest classifications.return_detections(bool) (required): Ask the vision service to return its latest detections.return_object_point_clouds(bool) (required): Ask the vision service to return its latest 3D segmentations.extra(Mapping[str, Any]) (optional): Extra options to pass to the underlying RPC call.timeout(float) (optional): An option to set how long to wait (in seconds) before calling a time-out and closing the underlying RPC call.
Returns:
- (viam.services.vision.vision.CaptureAllResult): A class that stores all potential returns from the vision service. It can return the image from the camera along with its associated detections, classifications, and objects, as well as any extra info the model may provide.
Example:
camera_name = "cam1"
# Grab the detector you configured on your machine
my_detector = VisionClient.from_robot(robot, "my_detector")
# capture all from the next image from the camera
result = await my_detector.capture_all_from_camera(
camera_name,
return_image=True,
return_detections=True,
)
For more information, see the Python SDK Docs.
Parameters:
ctx(Context): A Context carries a deadline, a cancellation signal, and other values across API boundaries.cameraName(string): The name of the camera to use for detection.opts(viscapture.CaptureOptions): Additional options to provide if desired.extra(map[string]interface{}): Extra options to pass to the underlying RPC call.
Returns:
- (viscapture.VisCapture): A class that stores all potential returns from the vision service. It can return the image from the camera along with its associated detections, classifications, and objects, as well as any extra info the model may provide.
- (error): An error, if one occurred.
Example:
// The data to capture and return from the camera
captOpts := viscapture.CaptureOptions{}
// Get the captured data for a camera
capture, err := visService.CaptureAllFromCamera(context.Background(), "cam1", captOpts, nil)
if err != nil {
logger.Fatalf("Could not get capture data from vision service: %v", err)
}
image := capture.Image
detections := capture.Detections
classifications := capture.Classifications
objects := capture.Objects
For more information, see the Go SDK Docs.
Reconfigure
Reconfigure this resource. Reconfigure must reconfigure the resource atomically and in place.
Parameters:
ctx(Context): A Context carries a deadline, a cancellation signal, and other values across API boundaries.deps(Dependencies): The resource dependencies.conf(Config): The resource configuration.
Returns:
- (error): An error, if one occurred.
For more information, see the Go SDK Docs.
DoCommand
Execute model-specific commands that are not otherwise defined by the service API.
For built-in service models, any model-specific commands available are covered with each model’s documentation.
If you are implementing your own vision service and add features that have no built-in API method, you can access them with DoCommand.
Parameters:
command(Mapping[str, ValueTypes]) (required): The command to execute.timeout(float) (optional): An option to set how long to wait (in seconds) before calling a time-out and closing the underlying RPC call.
Returns:
- (Mapping[str, viam.utils.ValueTypes]): Result of the executed command.
Example:
service = SERVICE.from_robot(robot, "builtin") # replace SERVICE with the appropriate class
my_command = {
"cmnd": "dosomething",
"someparameter": 52
}
# Can be used with any resource, using the motion service as an example
await service.do_command(command=my_command)
For more information, see the Python SDK Docs.
Parameters:
ctx(Context): A Context carries a deadline, a cancellation signal, and other values across API boundaries.cmd(map[string]interface{}): The command to execute.
Returns:
- (map[string]interface{}): The command response.
- (error): An error, if one occurred.
Example:
// This example shows using DoCommand with an arm component.
myArm, err := arm.FromRobot(machine, "my_arm")
command := map[string]interface{}{"cmd": "test", "data1": 500}
result, err := myArm.DoCommand(context.Background(), command)
For more information, see the Go SDK Docs.
FromRobot
Get the resource from the provided robot with the given name.
Parameters:
robotRobotClient (required)nameString (required)
Returns:
For more information, see the Flutter SDK Docs.
GetResourceName
Get the ResourceName for this instance of the Vision service with the given name.
Parameters:
name(str) (required): The name of the Resource.
Returns:
- (viam.proto.common.ResourceName): The ResourceName of this Resource.
Example:
# Can be used with any resource, using an arm as an example
my_arm_name = my_arm.get_resource_name("my_arm")
For more information, see the Python SDK Docs.
GetProperties
Fetch information about which vision methods a given vision service supports.
Parameters:
extra(Mapping[str, Any]) (optional): Extra options to pass to the underlying RPC call.timeout(float) (optional): An option to set how long to wait (in seconds) before calling a time-out and closing the underlying RPC call.
Returns:
- (Vision.Properties): The properties of the vision service.
Example:
# Grab the detector you configured on your machine
my_detector = VisionClient.from_robot(robot, "my_detector")
properties = await my_detector.get_properties()
properties.detections_supported # returns True
properties.classifications_supported # returns False
For more information, see the Python SDK Docs.
Parameters:
ctx(Context): A Context carries a deadline, a cancellation signal, and other values across API boundaries.extra(map[string]interface{}): Extra options to pass to the underlying RPC call.
Returns:
- (*Properties)
- (error): An error, if one occurred.
For more information, see the Go SDK Docs.
Close
Safely shut down the resource and prevent further use.
Parameters:
- None.
Returns:
- None.
Example:
await component.close()
For more information, see the Python SDK Docs.
Parameters:
ctx(Context): A Context carries a deadline, a cancellation signal, and other values across API boundaries.
Returns:
- (error): An error, if one occurred.
Example:
// This example shows using Close with an arm component.
myArm, err := arm.FromRobot(machine, "my_arm")
err = myArm.Close(ctx)
For more information, see the Go SDK Docs.
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! If you have any other feedback please let us know:
We're sorry about that. To help us improve, please tell us what we can do better:
Thank you!